


- BRNN
- BRI News
- BRNN News
- Database
Official Documents Polices and Regulations
Inter-government Documents International Cooperation BRI Countries
Business Guide Economic Data BRI Data
Trade
Investment Projects Latest projects
Cases - Content Pool
"SmartBot", an open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to advancing the field of robotics, launched its inaugural issue. The journal covers various fields of intelligent robotics with a focus on the integration of robotics with artificial intelligence.
Related news: Chinese university launches English journal on robotics
Front cover

01 Editorial
Advancing Intelligent Robotics for a Smarter Future: Bridging Technology and Human Potential
Bradley J. Nelson

Innovation Driving Transformation: The year 2024 marked a critical juncture for robotics, particularly in the realm of medical applications. As highlighted in this issue, innovations such as robot-assisted embolization technologies and bio-integrated microrobots (BIMs) are transitioning from experimental prototypes to clinical solutions, promising to revolutionize minimally invasive procedures. The medical robotics market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.20%, underscoring the urgency for robust ethical frameworks and international standards. SmartBot is committed to addressing these challenges by fostering dialogue between researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1002/smb2.12018
02 Review Article
Bio-Integrated Microbots: Fabrication, Actuation and Biomedical Applications
Huaping Wang, Jiaxin Liu, Ruhao Nie, Qing Shi, Qiang Huang, Toshio Fukuda
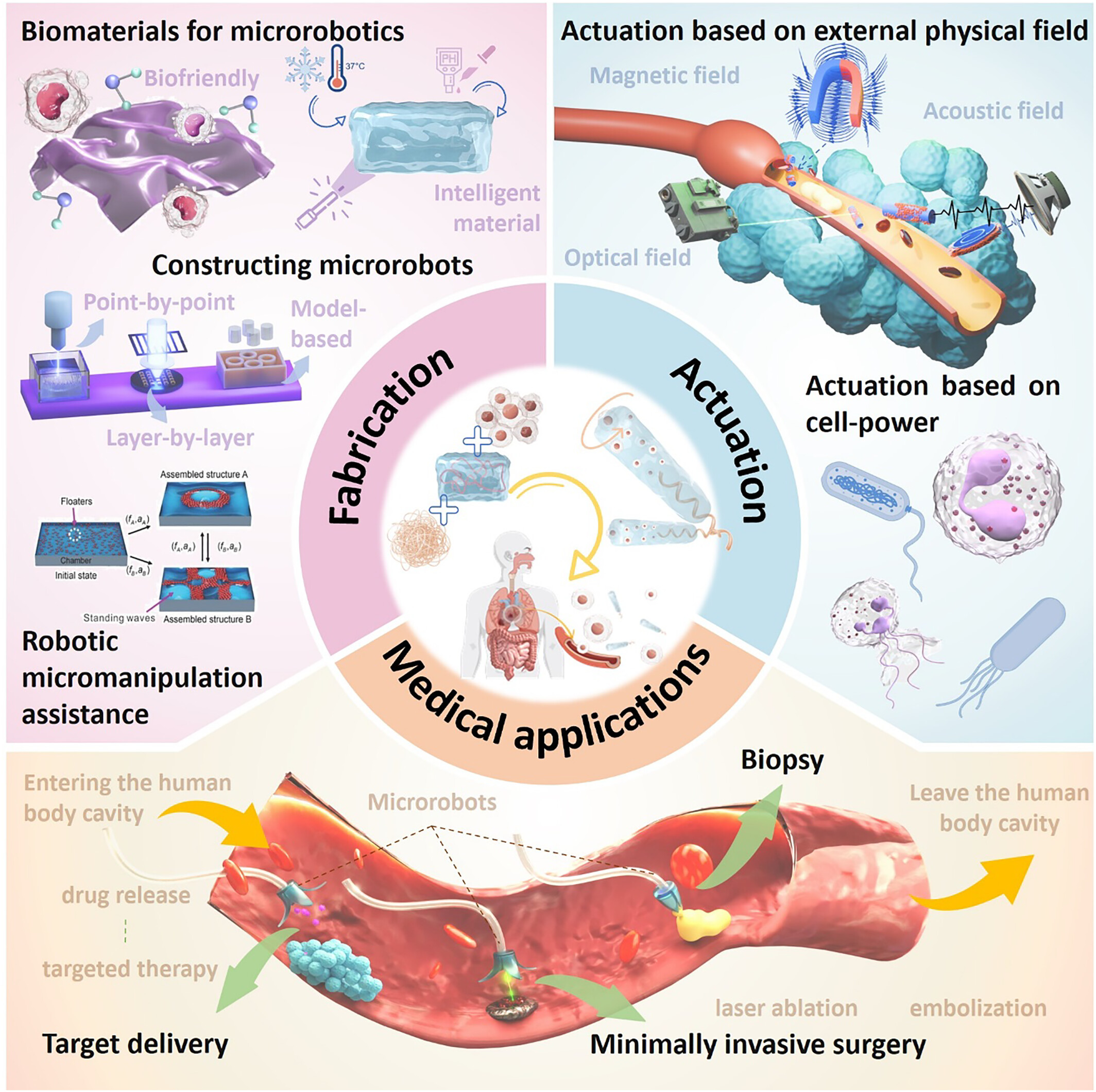
ABSTRACT: Bio-integrated microrobots (BIMs), which are fabricated with biofriendly materials, biological units (e.g. cells or biomolecules), or cell-material hybrids have emerged as a promising technology for minimally invasive biomedicine. The diminutive size and flexible structures enable BIMs to navigate within narrow, deep, and challenging-to-reach in vivo regions, performing biopsy, diagnostic, drug delivery, and therapeutic functions with minimal invasiveness. However, the clinical deployment of BIMs is a highly orchestrated task that requires consideration of material properties, structural design, locomotion, observation, therapeutic outcomes, and side effects on cells and tissues, etc. In this review, we review and discuss the latest advances in the bio-integrated microrobot domain, evaluating various methods associated with materials, fabrication, actuation, and the implementation of biomedical functions in BIMs. By comparing the advantages and shortcomings of these techniques, this review highlights the challenges and future trends in highly intelligent bio-integrated microrobots, which have huge potential in minimally invasive biomedicine.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1002/smb2.12007
03 Review Article
Motion-Force Interaction Performance of Parallel Robotic Mechanisms
Qizhi Meng, Andrés Kecskeméthy, Xin-Jun Liu
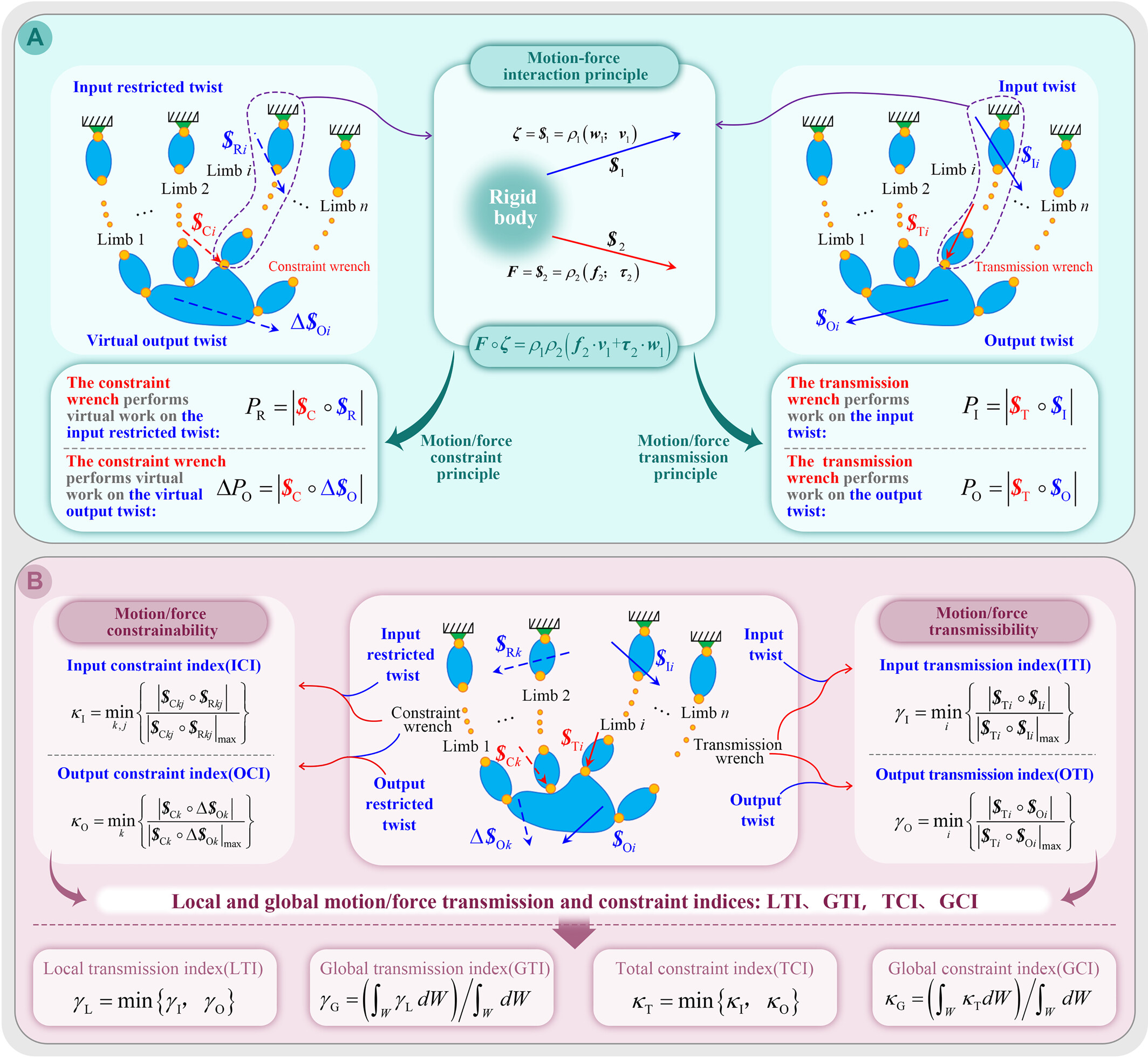
ABSTRACT: Parallel robotic mechanisms have emerged as a vital subfield in robotics science and engineering over the past few decades, receiving widespread attention and undergoing significant advancements. Despite extensive research encompassing type synthesis, dimension optimization, control theory, design principles, manufacturing techniques, and others, comprehensive reviews on the motion–force-related performance of parallel robotic mechanisms and their applications to real-world problems are still lacking. This review aims to fill this gap by analyzing and summarizing significant studies on the motion–force interaction performance of parallel robotic mechanisms. Examining the historical development of theoretical paradigms, the research of parallel robotic mechanisms began relatively late compared with their serial counterparts. Initially, approaches for parallel mechanisms were inherited or adopted from serial mechanisms. However, many cases have demonstrated that parallel robotic mechanisms possess unique characteristics, making it infeasible to directly transfer the theories developed for serial mechanisms to parallel mechanisms. Therefore, new methodologies are needed to properly analyze and evaluate the intrinsic properties of parallel robotic mechanisms, where the interaction between motion and force plays a crucial role. This paper offers an extensive and systematic review of the existing journal literature that analyzes and evaluates motion–force interaction performance of parallel robotics mechanisms, also known as motion/force transmission and constraint performance, providing a broad and detailed bibliography that will serve as a reference for the research community. The work examines research strategies, evaluation methods, performance indices, and real-world applications concerning the motion–force interaction performance of parallel robotic mechanisms, offering a foundation to stimulate future research and innovation.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1002/smb2.12006
04 Review Article
Robotic-Assisted Endovascular Embolization: Progress and Future Perspectives
Yusong Peng, Xurui Liu, Kai Fung Chan, Xin Song, Li Zhang
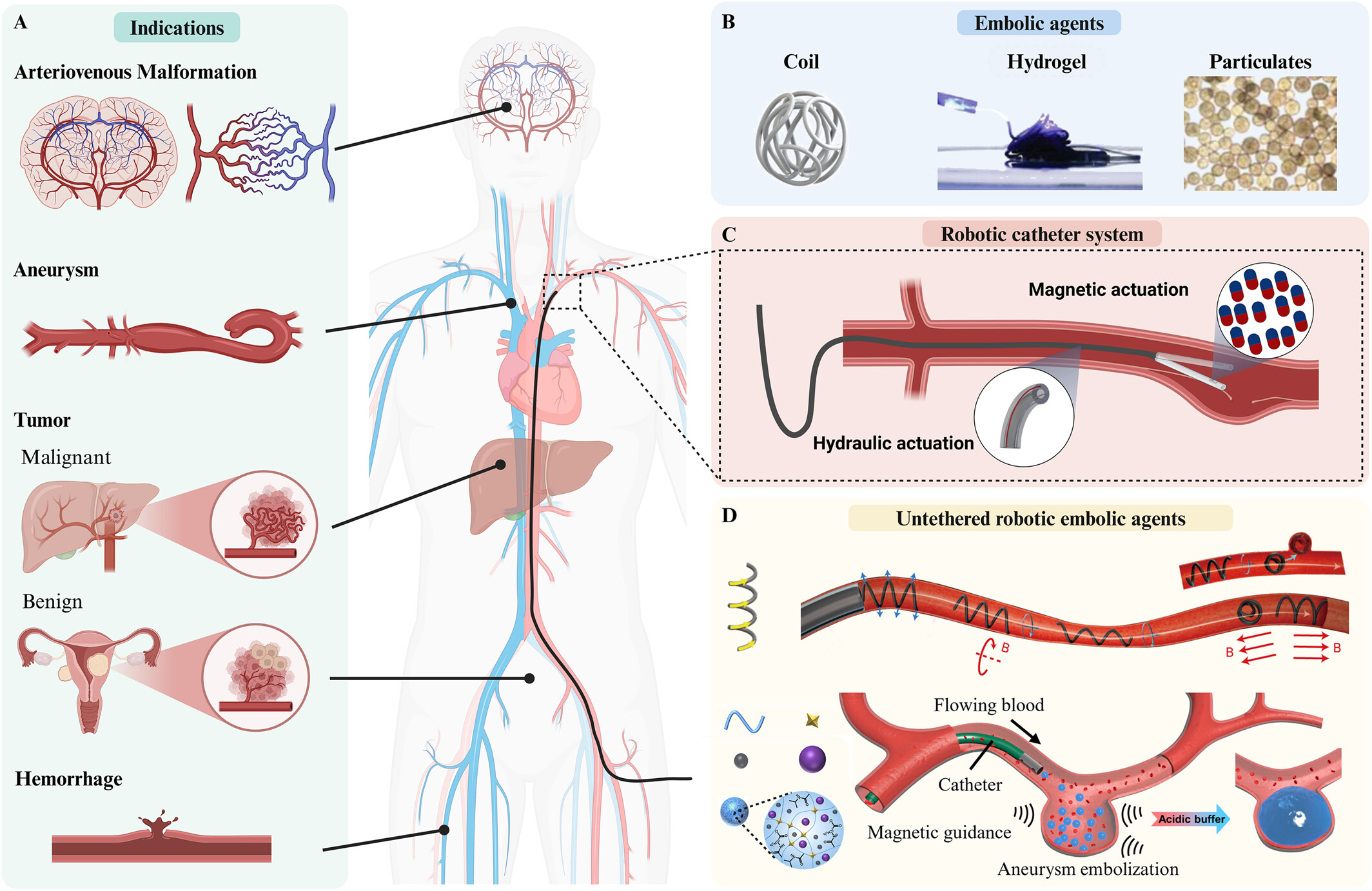
ABSTRACT: Minimally invasive transcatheter embolization is a widely utilized in interventional radiology to occlude blood vessels for treating a range of diseases and vascular injuries. Various embolic agents, such as metallic coils, microspheres, and liquid-based agents, are delivered to the target site to effectively block blood flow and achieve vessel occlusion. However, precise and selective deployment of these agents into target lesions remains a challenge due to the limited steerability and maneuverability of current catheter systems. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advancements in embolic agents and delivery devices, with a particular focus on emerging robot-assisted embolization technologies. It also discusses the key challenges associated with embolic materials and explores future trends shaping the field.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1002/smb2.12009
05 Review Article
A Comprehensive Review of Humanoid Robots
Qincheng Sheng, Zhongxiang Zhou, Jinhao Li, Xiangyu Mi, Pingyu Xiang, Zhenghan Chen, Haocheng Xu, Shenhan Jia, Xiyang Wu, Yuxiang Cui, Shuhao Ye, Jiyu Yu, Yuhan Du, Shichao Zhai, Kechun Xu, Yifei Yang, Zhichen Lou, Zherui Song, Zikang Yin, Yu Sun, Rong Xiong, Jun Zou, Huayong Yang
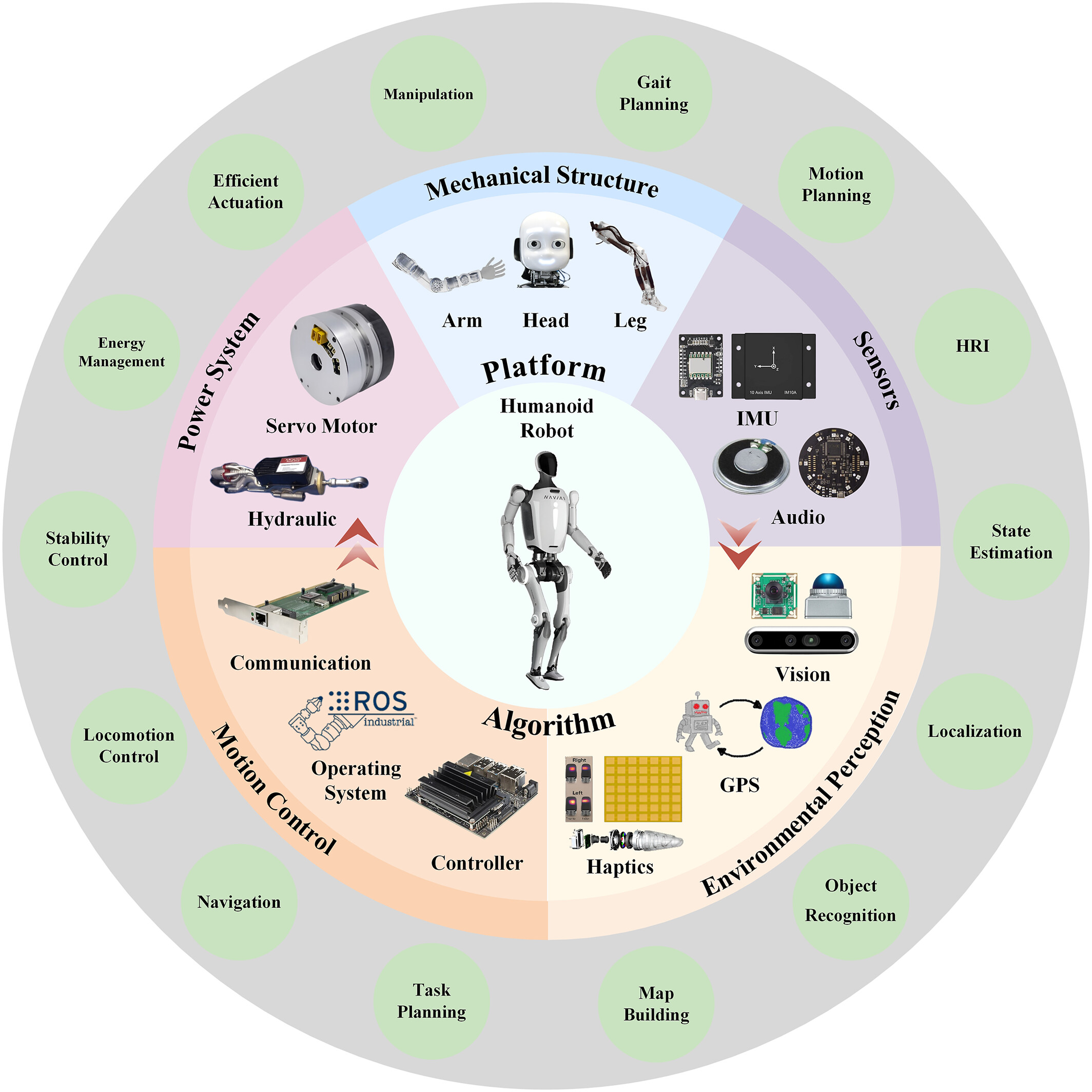
ABSTRACT: Humanoid robots, increasingly recognized for their potential to drive economic and social development, have garnered significant attention in recent years. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the progress, challenges, and future directions in humanoid robotics, with a particular emphasis on essential system components and key technological innovations. Through a review of historical milestones, this paper explores critical aspects such as the design of the head and body, and examines state-of-the-art technologies in areas like locomotion control, perception, and intelligent manipulation. By presenting a thorough analysis of the field, this work aims to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and inspire future innovations that will drive the continued evolution of humanoid robots.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1002/smb2.12008

Tel:86-10-65363107, 86-10-65368220, 86-10-65363106