


- BRNN
- BRI News
- BRNN News
- Database
Official Documents Polices and Regulations
Inter-government Documents International Cooperation BRI Countries
Business Guide Economic Data BRI Data
Trade
Investment Projects Latest projects
Cases - Content Pool
China, often referred to as "the world's factory," is now transitioning toward a smarter, more innovative industrial model. As traditional advantages such as low-cost labor and scale manufacturing lose ground to global competition and technological disruption, China is embracing smart manufacturing as a central strategy to upgrade its industrial base. By integrating digital technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and big data into manufacturing processes, the country aims to improve efficiency, product quality, and innovation capacity, ultimately moving up the global value chain.
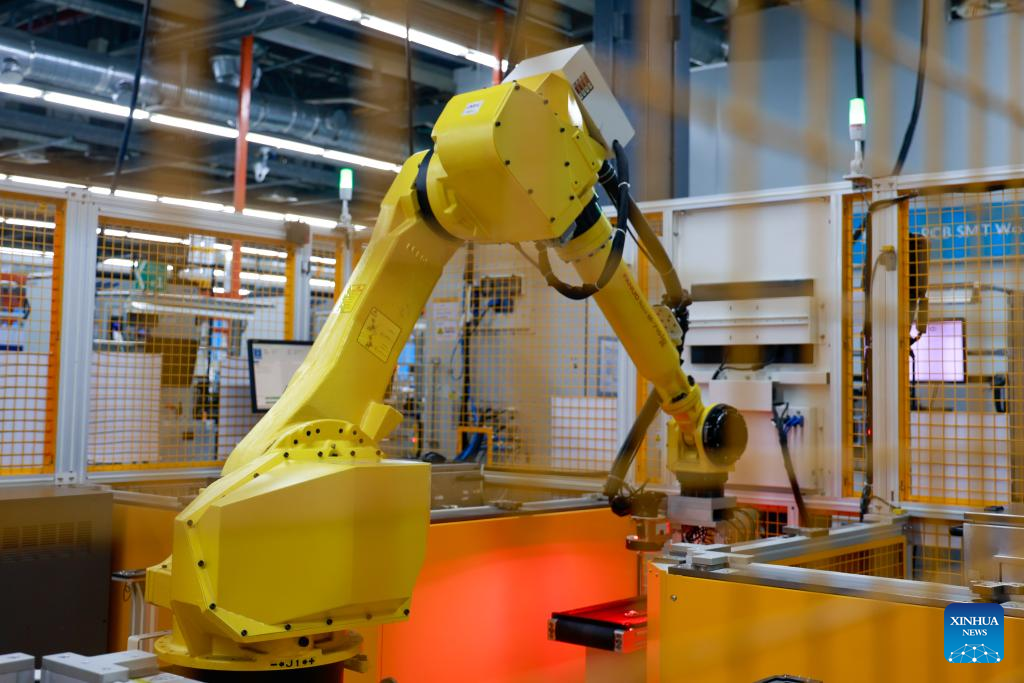

A robotic arm operates at an automated testing station of Jabil Circuit (Wuxi) Co., Ltd. at Wuxi Hi-Tech District Comprehensive Bonded Zone in Wuxi, east China's Jiangsu Province, on Sept. 15, 2025. (Xinhua/Liu Jiaqi)
Smart manufacturing refers to the digitization and automation of all stages of production, from design and research to factory floor operations, logistics, and servicing. The goal is not only to boost productivity, but also to reduce environmental impact, shorten innovation cycles, and enhance supply chain resilience. For China, this transformation is already well underway. According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), China has built over 30,000 smart factories, including around 1,200 at an advanced level and 230 recognized for excellence. These smart factories span more than 80 percent of the country's manufacturing sectors.
The results are significant. In China's highest-rated smart factories, development cycles have shortened by nearly 30 percent, production efficiency has risen over 22 percent, defect rates have halved, and carbon emissions have dropped by around 20 percent. Robotics is central to this transition. In places like east China's Shandong Province, many factories now feature fully automated assembly lines, with intelligent robots handling tasks ranging from materials transport to quality inspection. This large-scale adoption is made possible by China's expanding domestic capabilities in robotics and automation, which have made these technologies more affordable and scalable.
The rapid development of smart manufacturing in China is being driven by several key factors. First is strong state support through subsidies, policy guidance, and strategic plans. The government has created initiatives such as the "smart factory gradient cultivation program," encouraging firms to adopt advanced manufacturing techniques. Rising labor costs and the need for higher productivity have also pushed companies to invest in automation and digital tools. Additionally, the maturing of technologies like 5G, AI, and cloud computing has made smart manufacturing more accessible than ever. Environmental goals are another important driver, as China works to meet its carbon reduction targets by promoting energy-efficient, low-emission production methods.
The benefits of smart manufacturing are wide-ranging. For enterprises, it means faster time to market, lower defect rates, and more efficient use of labor and materials. For the environment, smart factories produce fewer emissions and generate less waste. On a broader scale, the shift enables China to move from producing low-cost, low-tech goods toward higher-value industries such as advanced machinery, electric vehicles, aerospace components, and medical devices. At the same time, it strengthens the resilience of supply chains, making them more agile and responsive to global shocks.
Globally, China's increasing export of automation technologies could lower barriers to smart manufacturing in other developing countries, influencing global industrial trends.
Smart manufacturing is reshaping the foundation of China's industrial economy. It is driving the next phase of industrial upgrading, allowing the country to improve its competitiveness, innovate faster, and reduce its environmental footprint.

Tel:86-10-65363107, 86-10-65368220, 86-10-65363106